In today’s internet-driven world, online privacy is more critical than ever. Whether you’re browsing social media, shopping online, or accessing work files remotely, your data is constantly being exchanged. That’s where a VPN (Virtual Private Network) comes into play. But how exactly does a VPN work?
In this in-depth guide, you’ll learn:
- What a VPN is
- How VPNs encrypt and protect your data
- The step-by-step journey of your data through a VPN
- Real-world examples and use cases
- Diagrams and videos to help you visualize the process
Let’s break it all down.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a service that encrypts your internet traffic and routes it through a remote server operated by the VPN provider. This process hides your IP address and makes your online actions more secure and private.
Key Functions of a VPN:
- Encrypts your internet connection
- Masks your IP address
- Bypasses geo-blocks and censorship
- Protects your data on public Wi-Fi
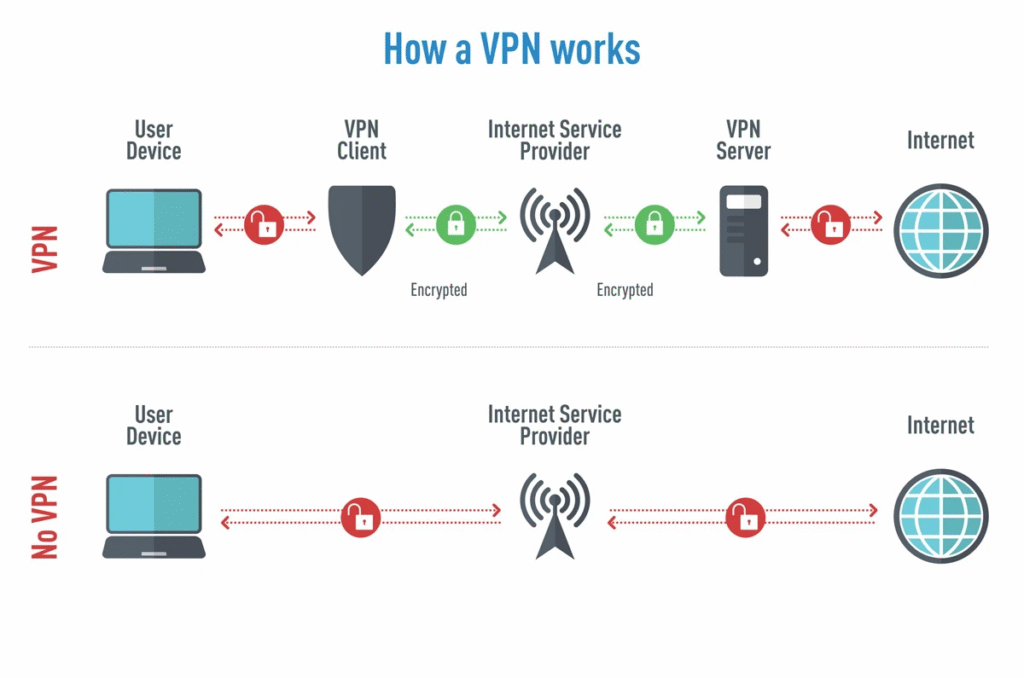
How VPNs Work: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Let’s break down what happens when you connect to a VPN:
Step 1: You Connect to the Internet
Your device (PC, phone, tablet) connects to the internet through your Internet Service Provider (ISP). Without a VPN, all your data passes directly through your ISP to the websites or services you’re using.
Step 2: You Launch the VPN App
When you open your VPN app and connect to a server, the VPN establishes a secure “tunnel” between your device and the VPN server.
Step 3: Your Data Gets Encrypted
Before leaving your device, all your internet traffic is encrypted using advanced encryption protocols (like OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard).
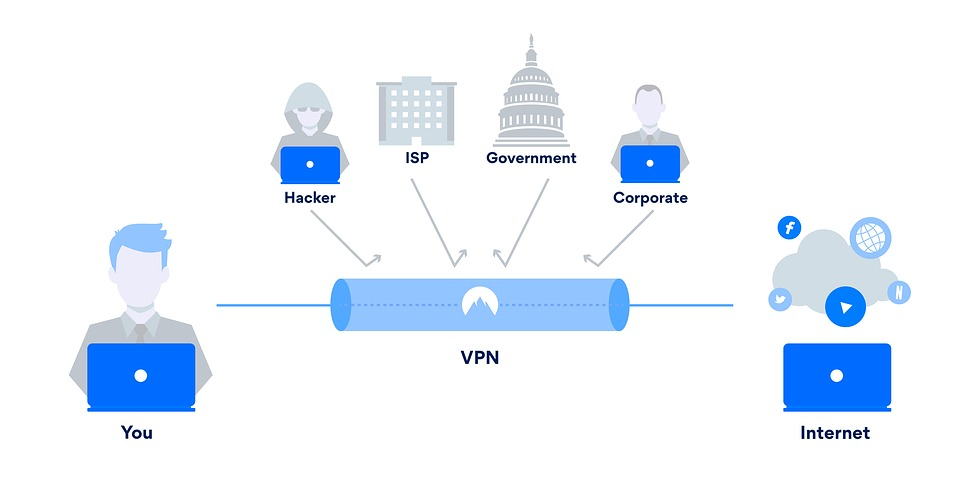
Step 4: Data Travels Through the Secure Tunnel
Instead of going directly to the internet, your data travels securely through the VPN tunnel to a VPN server. The VPN server masks your real IP address and replaces it with its own.
Step 5: VPN Server Sends Data to Destination
The VPN server forwards your encrypted request to the final destination (e.g., website or app). The website sees only the VPN server’s IP address, not yours.
Step 6: Data Returns Through the VPN
The website sends data back to the VPN server, which encrypts it again and routes it back through the secure tunnel to your device.
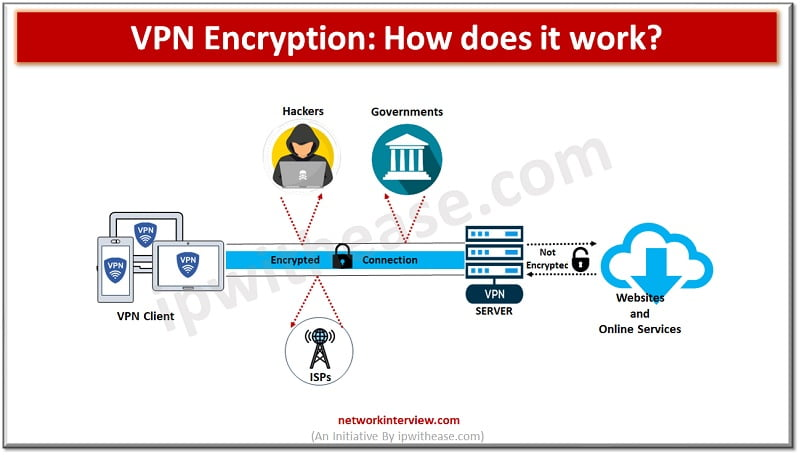
VPN Encryption Explained Simply
At the heart of a VPN is encryption — the art of converting data into unreadable code. Here’s a simple breakdown:
Types of Encryption Used in VPNs:
- AES-256: Military-grade encryption used by top VPNs
- ChaCha20: A fast, secure alternative for mobile devices
- RSA Keys: Used to securely exchange encryption keys
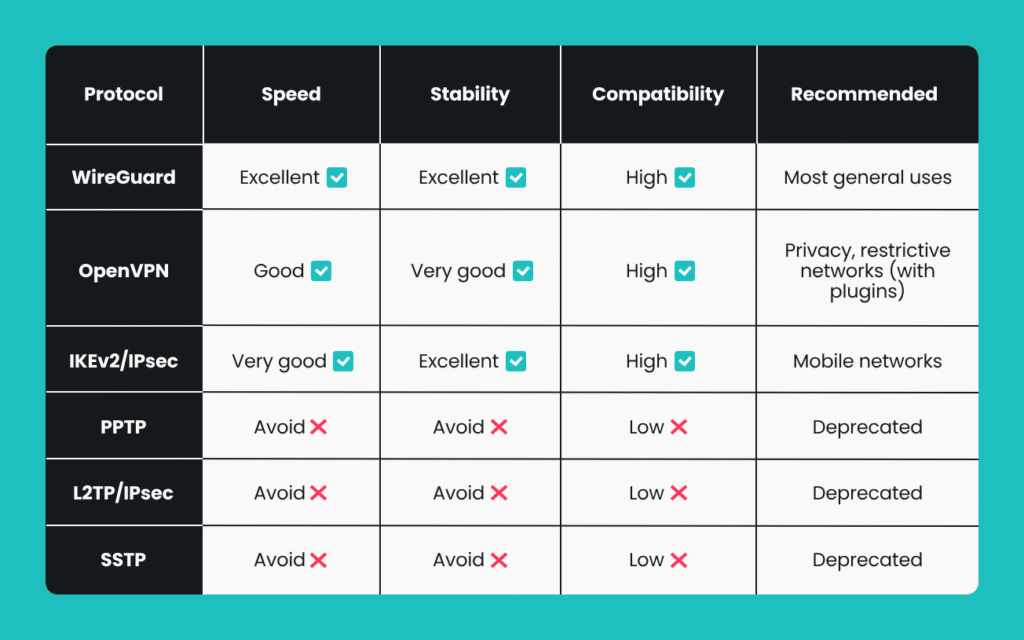
VPN Protocols: The Engine Behind the Scenes
A VPN protocol determines how the data is encrypted and transferred. Each protocol has its strengths and use cases.
| Protocol | Speed | Security | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | Moderate | Very High | Balanced use |
| WireGuard | Very Fast | High | Streaming, gaming |
| IKEv2 | Fast | High | Mobile devices |
| L2TP/IPSec | Slower | Medium | Legacy systems |
Real-World VPN Use Cases
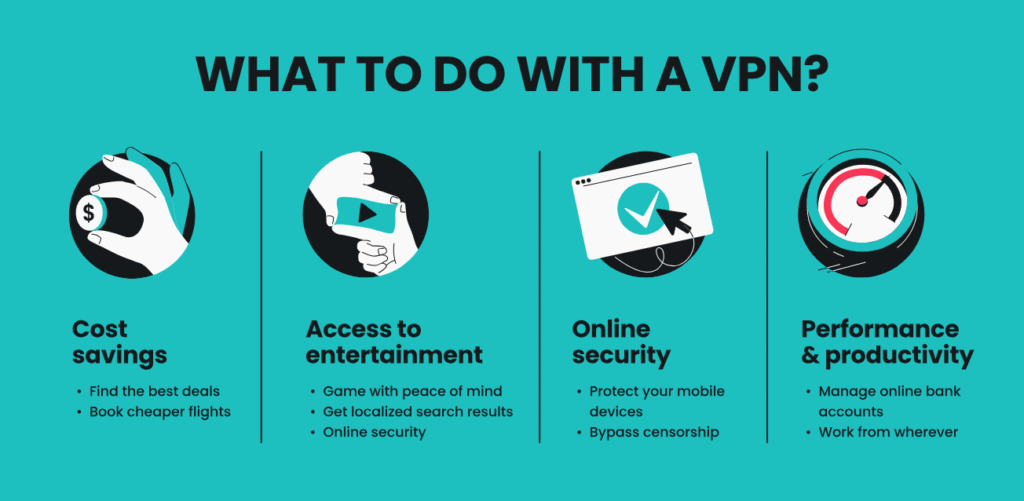
Using a VPN isn’t just for techies. Here’s how it benefits everyday users:
1. Protecting Data on Public Wi-Fi
VPNs secure your connection on open networks like coffee shops or airports.
2. Bypassing Geo-Restrictions
Access Netflix libraries, YouTube content, or websites not available in your country.
3. Preventing ISP Tracking
Your ISP won’t be able to log your online activity or throttle your speed.
4. Remote Work Security
Companies use VPNs to allow employees to securely access internal systems from anywhere.
5. Torrenting Safely
A VPN hides your IP and encrypts your activity when using P2P apps.
What Happens Without a VPN?
Without a VPN, your entire online activity is open to tracking and interception. Your:
- ISP can monitor and log everything you do
- IP address is exposed to websites and hackers
- Data on public Wi-Fi is vulnerable to cyberattacks
Common Myths About VPNs
❌ Myth 1: VPNs Make You 100% Anonymous
VPNs improve privacy, but they don’t make you invisible. Websites can still track you with cookies and browser fingerprints.
❌ Myth 2: VPNs Slow Down Your Internet
While some speed reduction may happen, premium VPNs offer optimized servers that minimize lag — especially with WireGuard protocol.
❌ Myth 3: Free VPNs Are Safe
Free VPNs often collect user data or display ads. For real privacy, always use a reputable paid VPN service.
How to Choose the Right VPN
When selecting a VPN, consider the following:
Features to Look For:
- No-logs policy
- Kill switch
- High-speed servers
- Support for multiple devices
- 24/7 customer support
VPNs and Your Digital Freedom
VPNs are essential tools in the fight for internet freedom and data security. With increasing censorship and cyber threats, more users are turning to VPNs for a safer online experience.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is using a VPN legal?
Yes, VPNs are legal in most countries, including the US, UK, and India. However, some countries (like China or Russia) restrict VPN use.
2. Can a VPN make me completely anonymous online?
Not entirely. A VPN hides your IP and encrypts your data, but websites can still use cookies and other trackers.
3. Will a VPN slow down my internet connection?
Some slowdown may occur, but high-quality VPNs minimize this with fast, nearby servers and modern protocols like WireGuard.
4. Do VPNs work on mobile devices?
Yes! Most VPN providers offer apps for Android and iOS with the same features as desktop versions.
5. Can I use a VPN for streaming services like Netflix?
Absolutely. Many VPNs help you bypass geo-restrictions and access content libraries in other countries.
Final Thoughts: Should You Use a VPN?
If you care about online privacy, data security, or uncensored access to the web, a VPN is an essential tool in your digital toolkit.
It doesn’t just hide your IP — it empowers you with control over your internet experience. And with today’s easy-to-use VPN apps, even beginners can enjoy safer browsing in minutes.

