VPN Slowing Down Your Internet? Here’s What to Do
Introduction
If you’ve ever wondered, “Is my VPN slowing down my internet?”, you’re not alone. Many users notice reduced speeds once they connect to a VPN. But encrypting and rerouting your data shouldn’t turn smooth browsing into frustration. In this comprehensive guide, you’ll learn why VPNs can slow things down—and exactly what to do to get your speed back while staying secure and private.
This actionable, SEO‑friendly article covers the most common causes, proven fixes, protocol considerations, and troubleshooting steps—helping your readers keep their online life fast and private.
Table of Contents
- Use WireGuard or faster protocol
- Choose a nearby or less crowded server
- Upgrade your VPN provider
- Switch to Ethernet over Wi‑Fi
- Adjust MTU, DNS, IPv6 settings
- Reduce encryption or use split tunneling
- Update apps and drivers
- [Conclusion & Take Action]
Why VPNs Can Slow Your Internet
A VPN adds encryption and an extra relay—two things that can degrade speed. Understanding the mechanics helps fix the problem:
- Encryption overhead adds processing time on both your device and the VPN server. Heavy encryption may reduce speed by up to 50 %.
- Routing via a remote server, especially one far from you, increases latency (the so‑called “trombone effect”).
- Server congestion: free or overloaded servers slow everyone down.
Yet VPNs can sometimes bypass ISP throttling—so in rare cases, connecting to a VPN may actually improve performance for throttled services.
Step‑by‑Step: Test Your VPN Speed
- Connect to your regular internet (disable VPN), then run a reliable speed test (speedtest.net, fast.com). Record download/upload speeds and ping.
- Connect your VPN, use the same server and test again. Compare differences.
- Repeat at different times and with different servers to see variation.
- Optional: use tools like iperf to test throughput via the VPN tunnel directly and isolate issues.
This comparison helps determine whether slowdowns stem from your ISP, Wi‑Fi, or the VPN setup itself.

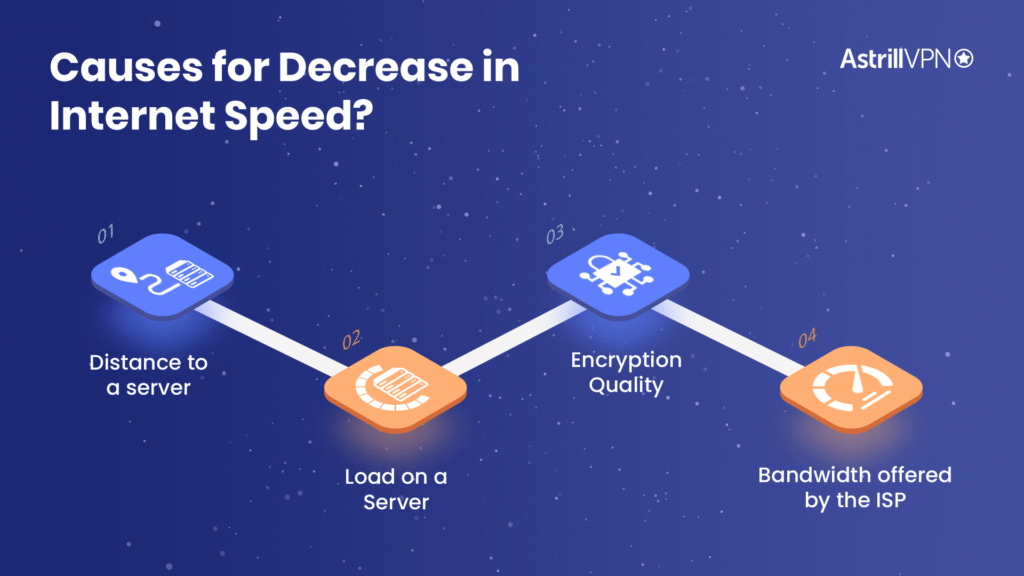
Top Causes of VPN Slowdown
Encryption & Protocol
- Common protocols: OpenVPN (UDP, TCP), IKEv2/IPsec, WireGuard, Lightway, Shadowsocks, PPTP.
- WireGuard consistently performs highest in speed tests, often doubling OpenVPN speeds .
- Strong encryption increases latency—lighter options may speed things up but at cost of privacy.
Server Location & Load
- Far‑away servers = higher latency.
- High‑traffic servers degrade speed. Opt for servers geographically close and with lower load .
Local Network & Device Issues
- Wi‑Fi versus Ethernet: Wi‑Fi interference or weak signal impacts VPN more visibly than direct connections.
- Device CPU/RAM limitations: encryption overhead may strain older hardware.
- System-level settings like MTU, IPv6, DNS, and proxy configurations can hinder performance.
How to Speed Up Your VPN (10 Proven Tips)
1. Use WireGuard or a Fast Protocol
Switch to WireGuard, Lightway, or IKEv2/IPsec if your provider supports them. Users on Reddit report ~2× faster speeds when switching from OpenVPN to WireGuard .
2. Choose a Nearby, Less Crowded Server
Connect to the closest server geographically or use the VPN app’s load info to select a less congested node. Servers farther away increase latency significantly r.
3. Avoid Free VPNs
Free services often offer poor performance, limited servers, and overcrowding—which slows speeds. Opt for reputable paid VPNs instead.
4. Use Ethernet Whenever Possible
Switch from Wi‑Fi to wired Ethernet to reduce latency and packet loss. Wi‑Fi is more susceptible to interference and signal issues that affect VPN tunneling.
5. Tweak System Settings (MTU, IPv6, DNS, Proxy)
- Adjust MTU—for example to ~1400—but test carefully.
- Disable IPv6 if not needed (can slow routing).
- Reset proxy and hosts file if misconfigured.
6. Enable Split Tunneling
Use split tunneling to route only specific apps through the VPN—reducing load and improving speed for other traffic.
7. Update All Software & Drivers
Keep your VPN client, network drivers, and OS updated. Developers frequently release speed improvements and bug fixes.
8. Close Background Apps
Ensure no background apps (cloud sync, updates, peer‑to‑peer) are consuming bandwidth while the VPN is active.
9. Test at Different Times & Servers
VPN speed can vary by server load and time of day. Try switching servers or testing during off‑peak hours.
10. Upgrade Your VPN or Internet Plan
If consistent slowness persists, consider upgrading your ISP or switching to a VPN provider with a global high‑capacity network.
When a VPN Can Improve Your Speed
Under certain conditions a VPN may actually improve performance:
- If your ISP is throttling specific traffic (like streaming or gaming), a VPN can hide the destination and bypass throttling.
- This is not common—but where ISPs apply selective throttling, VPN usage may yield faster throughput than connecting directly.
Recommended Fast VPNs of 2025
These VPN providers consistently deliver excellent speed and performance:
- Proton VPN (WireGuard) – Tested speeds up to ~1,200 Mbps; fastest overall in 2025 rankings
- ExpressVPN (Lightway) – Speeds up to ~1,600 Mbps on Windows; solid across devices .
- NordVPN (NordLynx) – Reliable ~901 Mbps with low latency and strong privacy reputation .
- Surfshark – Excellent value and speed (~848 Mbps) with unlimited device support .
For free-tier options, PrivadoVPN Free and Windscribe Free offer surprisingly fast speeds (500–900 Mbps) under light usage—but come with data caps or limited server access.
FAQ – VPN Speed Issues
Q1: Why is my VPN speed half of my normal internet speed?
A: Encryption and rerouting add overhead—expect some drop. But if it’s closer to ~50 % slower, check protocol, server load or network interference.
Q2: Is WireGuard really faster than OpenVPN?
A: Yes. WireGuard often doubles speeds compared to OpenVPN, thanks to leaner code and efficient encryption r.
Q3: Will switching to a nearby server always improve speed?
A: Yes, distance increases latency. For general browsing, local or regional servers offer significantly better performance.
Q4: Can a VPN make my internet faster?
A: Rarely—but yes, if your ISP throttles some traffic, a VPN may bypass that throttling and improve throughput.
Q5: How do I know whether slowness is from Wi‑Fi or VPN?
A: Test speed on wired Ethernet without VPN. Then connect VPN and test again. If Wi‑Fi alone is slow, focus on router placement, interference and signal strength first.
Q6: Are free VPNs always slower than paid ones?
A: Generally yes—free providers have fewer servers, overcrowding, and fewer optimization features. Paid VPNs often deliver far better and more consistent speeds.
Conclusion & Take Action
A VPN will always add some speed overhead—but with the right setup, the difference can be minimal. Here’s your action checklist:
- Test your speed with and without VPN.
- Switch to a fast protocol like WireGuard.
- Connect to nearby, low‑load servers.
- Use wired connections if possible.
- Adjust system settings (MTU, IPv6, DNS) and update software.
- Choose a reputable VPN provider for best performance.
By following these tips, you can get back most of your original speed—while staying secure, private, and able to stream, browse, and torrent without compromise.








