Introduction
Today’s digital world exposes us to threats—from hackers on public Wi‑Fi to ISPs, advertisers, and governments tracking our every move. That’s where a VPN—or Virtual Private Network—comes in. At VPN AdWiser, we believe everyone deserves online privacy, security, and freedom. In this guide, we’ll explain what a VPN is, how it works under the hood, why it matters, and how to choose one. Whether you’re new to VPNs or looking to understand their mechanics, this article delivers.
What Is a VPN?
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, is a technology that:
- Creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and a VPN server
- Masks your real IP address, making it appear as if you’re browsing from the VPN server’s location
- Encrypts data in transit, keeping it safe from eavesdroppers, ISPs, and public Wi‑Fi vulnerabilities
Why “virtual private network”?
- Virtual, because it uses the public internet to simulate a private connection
- Private, because traffic is encrypted and origin is hidden
- Network, because the VPN provider’s servers provide exit nodes to the wider internet
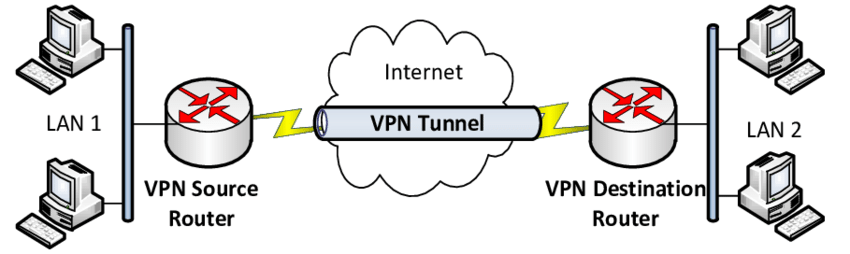
How Does a VPN Work?
Step‑by‑Step Tunnel Breakdown
- You open a VPN app on your device and connect to a VPN server.
- The VPN software establishes an encrypted tunnel between your device and the VPN server.
- All your internet requests are encrypted and routed through that tunnel.
- The VPN server decrypts the data, forwards your requests to the destination (e.g. a website), and returns responses through the tunnel.
- Your device decrypts the incoming traffic. At no point can your ISP or public Wi‑Fi see your actual browsing content—they only see encrypted data expected to go to the VPN server .
Masking Your IP Address & Location
- Your real IP address is hidden. The destination website only sees the VPN server’s IP address and location.
- You appear to be browsing from the VPN server’s country, allowing access to geo‑restricted content.
Encryption & Decryption Process
- VPNs use encryption algorithms (commonly AES‑256) to scramble your data.
- Only your device and the VPN server possess the decryption key. Intercepted traffic appears as gibberish.
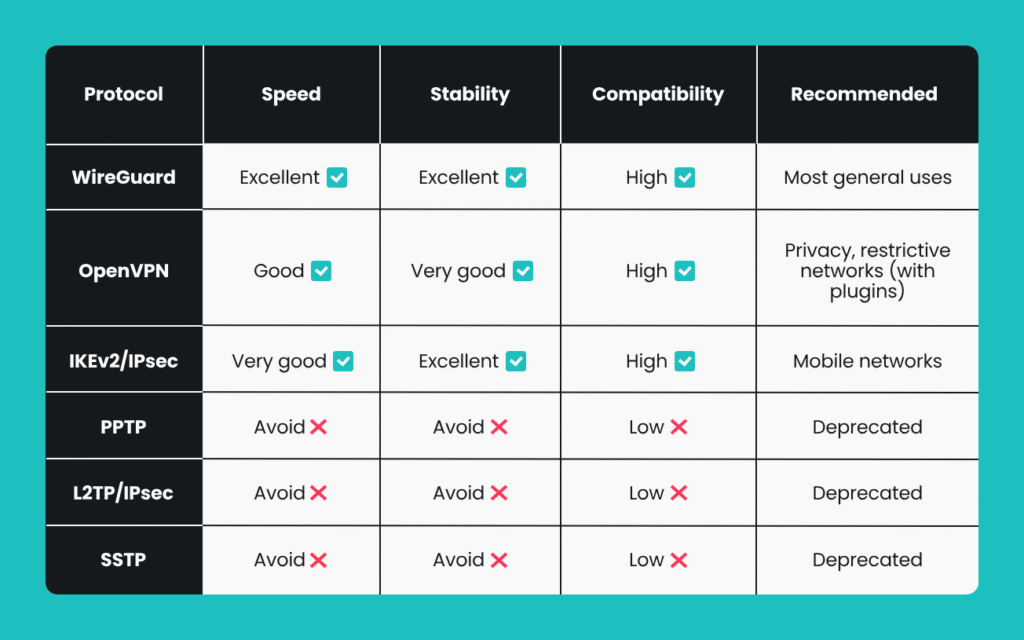
Protocols Explained
Common VPN protocols include:
- OpenVPN (TCP/UDP): Widely supported, highly secure
- IKEv2/IPsec: Fast, stable, and built into many operating systems
- WireGuard / NordLynx: Lightweight, faster, next‑generation protocol with excellent speed and security
- Proprietary protocols, like Lightway, NordWhisper, designed to circumvent VPN blocks or detect filters
Main Benefits of Using a VPN
1. Privacy & Anonymity
- Your ISP or local network can’t see your browsing history or destinations. Only the VPN server appears in logs.
- Websites and trackers can’t tie activity to your real IP.
2. Secure Public Wi‑Fi Use
- When using unsecured hotspots, without a VPN your data is open to snooping. With a VPN, data remains encrypted until it reaches the remote server.
- Eavesdroppers only see the encrypted tunnel.
3. Geo‑Restriction & Streaming Access
- Stream content from Netflix, BBC iPlayer, Disney+, or streaming services blocked in your region by virtually appearing in a supported country.
- Surfshark, NordVPN, ExpressVPN excel at this use case in 2025.
4. Bypass Censorship & Government Filtering
- In regions with heavy internet filtering, VPNs conceal traffic and bypass blocked sites by looking like regular encrypted web traffic.
- Features like NordWhisper are designed to defeat VPN detection.
5. Enhanced Security for Remote & Corporate Access
- Companies use VPNs for secure remote access to internal systems, remote work setups, or site‑to‑site connections.
- Authentication may include passwords, certificates, or two‑factor authentication.
Protocols, Encryption & Split Tunneling
In‑Depth Look: Protocol Comparison
| Protocol | Encryption Strength | Speed | Platform Support | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | AES‑256, strong | Moderate | Windows, macOS, Linux, routers | Classic, high‑compatibility |
| IKEv2/IPsec | AES‑256 or ChaCha20 | Fast | Mobile devices, newer OS versions | Mobile stability |
| WireGuard | ChaCha20, modern crypto | Very fast | Cross‑platform | Streaming, gaming |
| NordLynx / NordWhisper | Updated WireGuard builds | Blending into web traffic | NordVPN clients only | Anti‑VPN blocking, max speed |
Split Tunneling Feature
- Split tunneling lets you choose which apps or sites tunnel through VPN and which access local network directly.
- Useful for balancing speed and privacy—for example, streaming via VPN while accessing local banking on direct connection.
- Not all VPN services support this; Private Internet Access, Surfshark, NordVPN are among providers that do.
Use Cases: Who Should Use a VPN & Why?
Streaming & Geo‑Access
- Many users use VPNs to access exclusive content libraries (Netflix US, Hulu, BBC iPlayer).
- VPN AdWiser reviews show Surfshark and NordVPN consistently unblock streaming platforms in 2025.
Torrenting & File Sharing
- VPN adds anonymity and encryption to peer‑to‑peer file transfers.
- Prevents IP exposure to other peers or copyright monitors.
Privacy‑Conscious Browsing
- Ad‑trackers, ISPs, and governments track browsing habits. A VPN hides these footsteps.
- GDPR and data mining concerns make VPNs more necessary than ever.
SEO & Market Research (SEO-specific professionals)
- SEO pros use VPNs to simulate queries from different countries to test local SERPs and ad appearances.
- VPN helps research local keyword intent and competitor campaigns.
Remote Work & Corporate Access
- Securely access company intranets, shared servers, email, and internal tools.
- Supports site-to-site VPNs for branch offices and remote workforce.
Pros & Cons of Using a VPN
Pros 🌐
- Strong encryption and privacy
- IP masking and location spoofing
- Secure usage on public Wi‑Fi
- Access geo‑blocked content
- Protects against network throttling and tracking
Cons
- Possible speed reduction depending on server distance and protocol
- Depends on trust in VPN provider — choose audited, no‑logs services
- Not foolproof — features like DNS leaks or poor split tunneling can expose requests
- Some networks block VPN traffic, though stealth protocols like NordWhisper can help
Choosing the Right VPN
What to Look For
- Logging policy: Prefer strict no‑logs, independently audited providers.
- Encryption & Protocols: AES‑256, support for WireGuard or custom fast protocols.
- Server network: Wide global coverage ensures better performance and access.
- Streaming & P2P support: Choose providers optimized for Netflix, torrenting, etc.
- Speed & performance: Consider WireGuard or proprietary fast protocols.
- Security extras: Kill switch, DNS leak protection, split tunneling.
- Device support: Windows, macOS, Linux, iOS, Android, router compatibility.
- Reputation & audits: Independently verified providers rank better.
- Customer support & money‑back guarantee.
Leading VPN Providers in 2025
- NordVPN: Strong encryption, NordLynx/WireGuard support, NordWhisper to beat VPN blocking. TechRadar calls it the best overall.
- Surfshark: Excellent value, unlimited devices, great for streaming. Ranked top by Tom’s Guide.
- ExpressVPN: Easy to use, blazing speed, media‑streaming consistency. TechRadar praises its quantum‑resistant encryption.
- Proton VPN: Free tier, SecureCore routing, audited privacy, ideal for privacy‑conscious.
- Private Internet Access (PIA): Strong court‑tested privacy, flexible split tunneling, Linux support.
FAQs
Q1: What exactly does a VPN protect?
A VPN encrypts your internet traffic and masks your IP—protecting privacy on public Wi‑Fi, hiding browsing history from your ISP, and securing your identity when torrenting or browsing tracking‑heavy sites.
Q2: Will using a VPN slow down my internet?
Possibly. Encryption and server distance can add latency. However, modern protocols like WireGuard and services with global servers mitigate slowdowns significantly.
Q3: Can a VPN be blocked?
Yes; some networks (e.g. schools, restrictive governments) detect and block VPN traffic. Providers with stealth or obfuscation protocols (like NordWhisper) bypass this blocking.
Q4: Is VPN usage legal?
Yes in most countries—VPNs are legal in India and most of the world. However, in a few countries (e.g. China, Russia, UAE), usage may be restricted or regulated.
Q5: What is split tunneling?
Split tunneling allows specific apps or websites to use the VPN tunnel while others access the internet normally. Useful to avoid routing local traffic unnecessarily through VPN.
Q6: What is a DNS leak and why does it matter?
A DNS leak happens when DNS requests bypass the VPN tunnel, going to your ISP instead. It reveals visited domains even though content stays encrypted. Leak protection is essential.
Q7: Can I torrent safely with a VPN?
Yes—VPN masks your IP and encrypts transfers. But choose providers that explicitly allow P2P traffic and have strong privacy policies.
Conclusion
A VPN is a powerful tool for enhancing privacy, securing public connections, bypassing geo‑restrictions, and conducting anonymous browsing. It works by creating an encrypted tunnel between your device and a VPN server—hiding your IP and encrypting your data with robust protocols like AES‑256, OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard. While some disadvantages exist—like potential speed loss or dependence on provider trust—the benefits far outweigh the risks for most users.
At VPN AdWiser, our mission is to help you choose the right VPN—whether for streaming, torrenting, or privacy. Stay secure, remain private, and enjoy full online freedom.